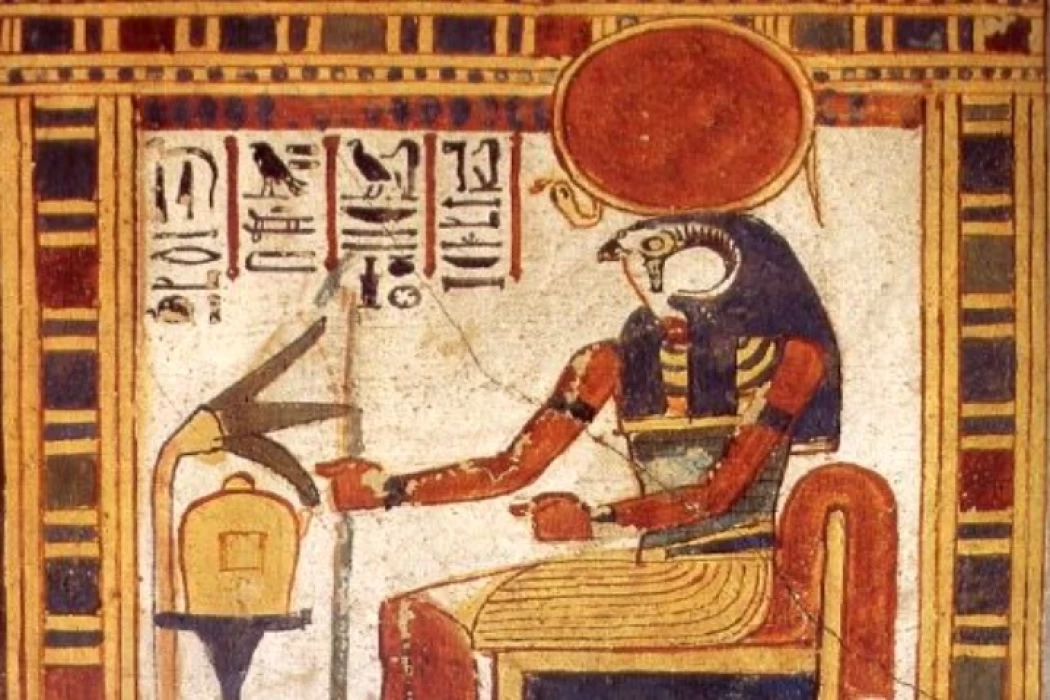
Ra, el Dios Creador del Antiguo Egipto
Ra, el dios del sol, tiene tres apariciones: Khepri por la mañana, Ra al mediodía y Atum al atardecer. Es imposible determinar el momento histórico en que la doctrina del sol abrazó los conceptos de la nueva monarquía, y las primeras pruebas en este campo aparecen en el nombre del segundo rey de la segunda dinastía (Ra - Nab), que significa (Ra el maestro), y el rey (Zuser) de la tercera dinastía llevaba el título ( Ra el Dorado) y parece que ambos reyes anteriores se unieron a (Ra), aunque como sus hijos, pero esa unificación no fue a largo plazo ya que los reyes posteriores la abandonaron, entonces (Khafra y Menkaure) de la Cuarta Dinastía fueron los dos primeros reyes en añadir el título ( Ibn Ra), que significa (hijo del sol), a sus títulos.
Ese título también fue llevado por tres reyes cerca del final de la Quinta Dinastía (Ni, Serra, Jed Karea y Unas), luego ese título se convirtió en una parte inseparable de los nombres de los reyes desde la Sexta Dinastía hasta el final de la historia del antiguo Egipto, ya que este título fue precedido por el nombre personal del rey que nació con él Así, se hizo evidente que el rey era considerado desde su nacimiento como hijo del dios (Ra), y antes de eso y desde el rey (el abuelo de una rama) de la Cuarta Dinastía, los nombres de los reyes de algunos de esta familia fueron compuestos del nombre (Ra), a veces desde su nacimiento o al ascender al trono si El nombre de nacimiento no incluía el elemento compuesto del dios (Ra).
Según una leyenda tardía, los reyes de la V Dinastía eran hijos del dios (Ra), y según una leyenda tardía, los reyes de la V Dinastía eran hijos del dios (Ra) de la esposa de un sacerdote del sol, una historia que refleja la victoria de la doctrina del sol durante la época de esta familia cuyos reyes construyeron templos al sol similares al modelo del antiguo Templo del Sol en Heliópolis.
Lo cierto es que, aunque la posición única del dios (Ra) había empezado a decaer un poco hacia finales de la V Dinastía, su creencia ya había penetrado en el núcleo de la religión egipcia, y muchas deidades locales se encontraban con (Ra). En las primeras escenas se representaba claramente al halcón (Horus de Edfue) revoloteando sobre la cabeza del rey, pero esta escena cambió después, y el disco solar alado protegía con sus alas el título del Alto Egipto y del Bajo Egipto. El disco alado representa al rey real, y lleva uno de sus títulos (el gran dios.) ) que se asocia con el nombre del rey y todo esto decide la mezcla completa entre (Ra y Horus) y el rey en la doctrina de la monarquía sagrada.
Egipto es el mejor destino para pasar unas vacaciones extraordinarias, visite la guía de viajes de Egipto, para aprender más sobre la gran y muy larga historia del país, ya que proporcionamos a nuestros clientes toda la información y los detalles necesarios. Experimente Egipto Tours con nuestro equipo que le ayudará a descubrir un montón de cosas que hacer en Egipto. Disfrute de un refrescante crucero por el río Nilo durante los tours de Navidad en Egipto o durante los increíbles tours de Semana Santa en Egipto.
Ra, the sun god, has three appearances; Khepri in the morning, Ra at noon, and Atum at sunset. It is impossible to determine the historical moment in which the doctrine of the sun embraced the concepts of the new monarchy, and the early evidence in this field appears in the name of the second king of the second dynasty (Ra - Nab), which means (Ra the master), and the king (Zuser) of the third dynasty bore the title ( Ra the Golden) and it seems that both previous kings united themselves with (Ra), albeit as his sons, but that unification was not long-term as the subsequent kings abandoned that, then (Khafra and Menkaure) of the Fourth Dynasty were the first two kings to add the title ( Ibn Ra), meaning (son of the sun), to their titles.
That title was also borne by three kings near the end of the Fifth Dynasty (Ni, Serra, Jed Karea, and Unas), then that title became an inseparable part of the king’s names from the Sixth Dynasty until the end of ancient Egyptian history, as this title was preceded by the personal name of the king who born with it Thus, it became apparent that the king was considered from his birth as a son of the god (Ra), and earlier than that and since the king (the grandfather of a branch) of the Fourth Dynasty, the names of the kings of some of this family were compounded from the name (Ra), sometimes from their birth or when ascending the throne if The birth name did not include the compound element of the god (Ra).
According to a late legend, the kings of the Fifth Dynasty were children of the god (Ra), and according to a late legend, the kings of the Fifth Dynasty were children of the god (Ra) from the wife of a priest of the sun, a story that reflects the victory of the doctrine of the sun during the era of this family whose kings built temples to the sun similar Model of the ancient Sun Temple in Heliopolis.
The truth is that although the unique position of the god (Ra) had begun to decline somewhat near the end of the Fifth Dynasty, his belief had already penetrated into the core of the Egyptian religion, and many local deities were found with (Ra). In the early scenes, the falcon (Horus of Edfue) was depicted clearly as it fluttered over the head of the king, but this scene changed after that, and the winged sun disk protected with its wings the title of Upper Egypt and Lower Egypt. The winged disk represents the actual king, and it bears one of his titles (the great god). ) which is associated with the name of the king and all of this decides the complete mixing between (Ra and Horus) and the king in the doctrine of the sacred monarchy.
Functions and Origin
Re (or Ra, in Coptic: RīŇu "He who makes") is the sun god. He is the primordial God, the originator of all things. He is the Lord of infinity, creator of Heaven and Earth, the first to come into existence before all that exists, the one who created himself. The meaning of his name is uncertain. It is believed that this was not a word for "sun," but may have been a variant of the words meaning "creative force" and "creator." It was during the Old Kingdom (2647-2150) that he became a principal deity. More specifically, during the Fifth Dynasty (2465-2323), he was elevated to the rank of national deity and subsequently linked to the Theban god Amun to become Amun-Re, the principal deity of the Egyptian pantheon. King Khafre (or Khafre, 2518-2492) was the first to include the name Sa-Re, "The Son of Re," in his title.
He was born from a primeval ocean of his own volition, landed on a hill, the primeval hill, and rose on the Benben stone in Heliopolis, a stone that would later serve as a model for future obelisks. Re is associated with creation, whether original (the creation of the world), or annual with the awakening of nature in spring. He was therefore venerated as creator and protector. He is therefore the master of the seasons and also the judge of the divine and terrestrial worlds. Like the sun, Ra was the one who allowed the world to exist and develop, because without the sun there is no life, and therefore without Ra there could be no life either. He was considered the father of all the Gods and by extension, the creator of all men.
His divine qualities include the sun disk, which represents stability and longevity.
▪ He was linked with the bull and the ichneumon, a snake-hunting mongoose. These were his sacred animals. There were also the cat and the scarab, which, while not sacred, were associated with him.
▪ His emblems: The Was scepter, a sign of strength and power; The obelisk, which recalls the first Earth on which the Salera of creation arose.
▪ His color and element: Fire and red, the color of fearsome violence and a burning hue.
The Egyptians believed that after a long reign over mankind, Ra grew old and had to face their rebellion. His daughter Tefnut repressed her, but now vulnerable, he decided to reach the heavens. When he called her back to him, she changed into the celestial cow Hathor, creating the celestial vault that would eventually hold the solar boat and its heavenly retinue—now represented by the stars—in her womb.
He took different forms and names throughout his journey. He was: Khepri-Ra (The Scarab), "the one who is becoming" or "the one who comes into existence of himself," in the morning at the rising sun; Re-Horakhty (The Sun). At nightfall, Re changed boats to bring light and warmth to the afterlife and reappeared in the East each morning for the living. The Pharaoh, after his death, took his place on Re's boat to return to the realm of the dead.
According to George Hart, the ancient Egyptians, with their complex polytheistic beliefs, worshipped Re as the creator god, particularly his followers at Heliopolis. They believed that when Re wept, from his tears came mankind. These followers believed that Re created himself, while the followers of Ptah believed that Re was created by Ptah. This is thought to be why the Old Kingdom (2647-2150) pyramids at Heliopolis rarely mention Re. In one passage in the Book of the Dead, Re cuts himself and his blood transforms into two intellectual personifications: Hu, authority, and Sia, spirit.
Its main places of worship were:
Heliopolis, in Lower Egypt (Heliopolis is the Greek word for helios = sun), which was the capital of the cult of Ra during the time of the first dynasties, when the city was called Yunus (or Onu-Yunus "City of the Pillar") and where he was identified with the local sun god Atum.
Abu Gurad (or Abu Gurab), south of Cairo. The ruins that remain on the site today hardly allow us to imagine the scale of the five religious complexes that the kings of the Fifth Dynasty, from Userkaf (2465-2458) to Nyuserre. The largest was built by the latter.
Re was also venerated in major sanctuaries such as those at Dendera, Edfu, Hierakonpolis, and Karnak.
















