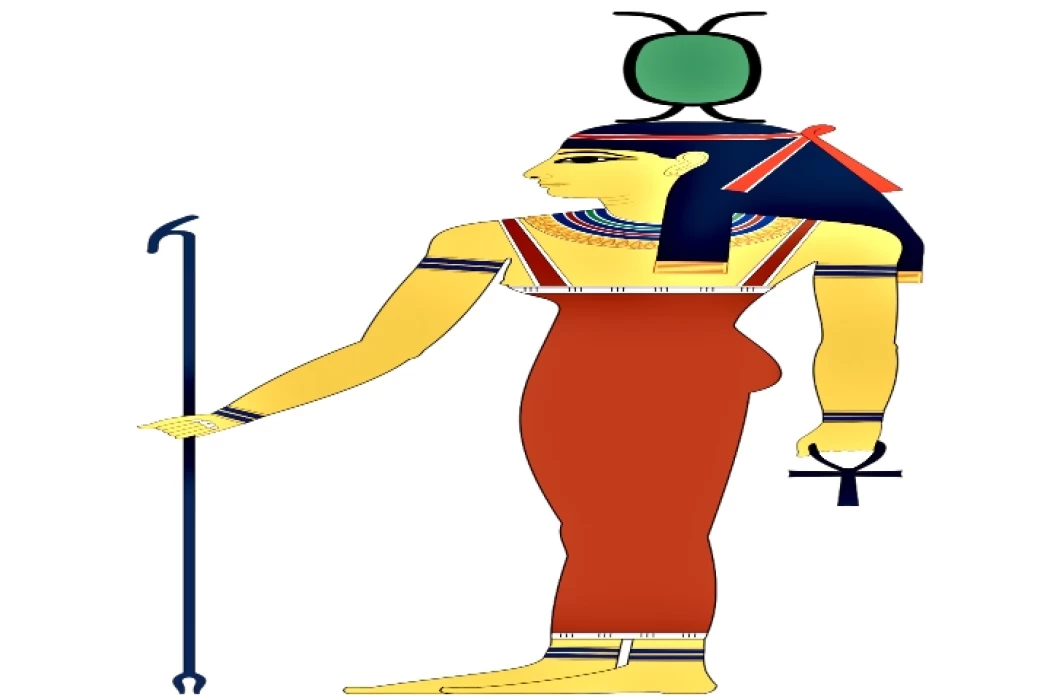
古埃及的网(奈丝)女神
西方之神——非也。 或 非也。(她的名字有两种拼写变体)古埃及的女神,对 镭 的崇拜种类繁多,有的说是(非也。)或(非也。),指的是点燃太阳的露水,有的说是(纽约)。拉——法老众神的统治者——而这个词在古埃及语中的起源则不同:nat 表示墙壁,nit 表示动词。这种情况可以与学者们达成一致,他们将她描述为布料和辉煌的女神,她的神圣标志(出现在利比亚纹身中)通常被描绘在头顶(作为织梭的象征)。
她是战争女神。女神(奈特)是一个完整的人类,但她携带一面带有两支交叉箭的盾牌,而带有两支交叉箭的盾牌是女神(奈特)的神圣物质象征,古代柏柏尔人专门用手臂上的纹身来装饰她,这从法老古物的遗迹中可以看出。
Lord of the West - No or No (there are two variants of the spelling of her name ) goddess in ancient Egypt Varieties of worship (no) or (nyt) by authorization summarizing the dew kindled from which the sun Ra - lord of the Pharaonic gods - and the origin of the word in the ancient Egyptian language on the other hand: the word in walls (nat) to walls (nit), which means the verb woven into this Case can be agreed with scholars who have described her as the goddess of cloth and splendor in her sacred signs (appearing in Libyan tattoos) and usually depicted above the head (as the symbol of the weaving shuttle).
She is the goddess of war. The goddess (Neith) was a full human being, but she carried a shield with two crossed arrows, and a shield carrying two crossed arrows is the sacred material symbol of the goddess (Neith), and the ancient Amazigh specialized in adorning her with tattoos of the arm alone, as is evident from the remains of pharaonic antiquities.
Name and Symbol
In Pharaonic texts, the goddess Neith is called "Lady of the West"—she is written Net or Neith—and, according to various Pharaonic texts, represents various goddesses born in different eras and stages of Pharaonic civilization.
The worship of Net or Neith is linked to a personification in the form of the primordial pool of water from which the sun god—the lord of the Pharaonic gods—Ra—emerged. The origin of the word in ancient Egyptian, on the other hand, is that if we trace the word "Net" back to the word "Nett," which means the verb "to weave," then we can accept the view of scholars who described her as a goddess of weaving and who saw in her sacred signs (which appear on Libyan tattoos) and are usually depicted above her head (as a symbol of a loom shuttle).
She is the goddess of war. The goddess Neith was seen with a shield with two crossed arrows on it, despite being a fully realized human being. The goddess Neith's sacred material symbol is a shield with two crossed arrows. The ancient Amazighs were unique in adorning themselves with her by tattooing her on their arms, to the exclusion of others, as appears from the remains of the Pharaonic monuments.
The Myth of the Goddess Net
Herodotus mentions that ancient Amazigh women danced in two divided groups, wearing war attire, in a horse-drawn dance around Lake Tritonis, currently located in the Gulf of Gabes in Tunisia. This was likely in honor of the goddess Athena, the Greek goddess, according to Plato.
Her Worship
The worship of Neith flourished in the later periods, beginning with the Twenty-sixth Dynasty, also known as the Saisian Dynasty. The kings of this dynasty had distant Libyan origins. The original home of her cult was the city of Sais, the capital of the Fourth and Fifth Districts in the Delta. Her worship spread to Upper Egypt after the political unification of the two regions, just as it had previously spread to the Delta.
Her characteristics are indistinguishable from those of Isis. Wes Budge says that the origin of this goddess, with her main characteristics, goes back to the Nile Delta and eastern Libya, and that her characteristics are represented by the rituals of procreation and reproduction. Dr. Rajab Abdel Hamid Al-Athram confirms that Neith in the western Delta is the same as Tanit in the Tripolitanian region. (See Lectures on the Ancient History of Libya.) In ancient times, she was called "the one who existed before existence."
In one of the commemorative texts, she says, describing herself: "I am everything that has existed—everything that exists—everything that will exist—and no one has ever been able to reveal my veil." However, the Egyptians applied these same attributes to Isis, but by the name "Athena," who says: "I was created from myself." The meaning of the word Neith or Net in ancient Egyptian is: "She or the existing one—or the one who came into existence." She is also described in Pharaonic texts as "the hidden one." (From the book "The Gods of the Pharaohs" by Wallis Budge. Translated by Youssef Ahmed Al-Khatali.)
Finally, we should point out that "the veil of Neith that no one removed" can be compared to the veil of the Greek goddess Persephone, which was found only in Libya! Indeed, Libyan archaeologist Professor Abdul Qader Al-Mazini asserts that "outside the city of Cyrene specifically, there is no statue of Persephone wearing a veil or with a face completely devoid of human features." Based on this, we can conclude that the ancient Libyans unified the veil of Neith with the veil of Persephone, the goddess of death and resurrection.















